本书为Primer C++ 中文第五版
练习题笔记

(a)
含义:检查string字符串的每一个字符
修改为:
string::iterator iter = s.begin();
while(iter != s.end());
或者
while( s.begin() != s.end());
(b)
含义:检查某个单词是否存在,如果不存在会执行什么操作
修改为:
bool status;
while(status = find(word)) {/*...*/}
if(!status) {/*...*/}

(5.5)
void transIf() {
int grade;
while(cin >> grade) {
if(grade >= 90) {
cout << "A" << endl;
}
else if(grade >= 80) {
cout << "B" << endl;
}
else if(grade >= 60) {
cout << "C" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "D" << endl;
}
}
}
(5.6)
void trans() {
int grade;
while(cin >> grade) {
(grade >= 90)? cout << "A" << endl :
(grade >= 80)? cout << "B" << endl :
(grade >= 60)? cout << "C" << endl : cout << "D" << endl;
}
}
(5.7)
a>
ival1 = ival2; //缺少分号
b>
//if部分有两行代码,需要加上花括号
c>
//int val; 应该定义在最前面,要不然作用域不能到达第二个if
d>
// = 是赋值符号,赋值总为true
// == 才是判断符号
(5.8)
/*
悬垂else是指当程序中的if分支多于else分支时,如何为else寻找与之匹配的if分支的问题。
C++规定,else与离它最近的尚未匹配的if匹配,从而消除了二义性。
*/

(5.9)
void count() {
string seq;
while(cin >> seq) {
int Cnt = 0;
string::iterator iter = seq.begin();
while(iter != seq.end()) {
if(*iter == 'a' || *iter == 'e' || *iter == 'i' || *iter == 'o' || *iter == 'u') {
Cnt++;
}
iter++;
}
cout << Cnt << endl;
}
}
(5.10, 5.11, 5.12)
void countSt() {
string seq;
while(getline(cin, seq)) {
int aCnt =0, eCnt = 0, iCnt = 0, oCnt = 0, uCnt = 0;
int blank = 0, t = 0, n = 0;
int ff = 0, fl = 0, fi = 0;
string::iterator iter = seq.begin();
while(iter != seq.end()) {
switch(*iter) {
case'a':
case'A':
aCnt++;break;
case'e':
case'E':
eCnt++;break;
case'i':
case'I':
iCnt++;break;
case'o':
case'O':
oCnt++;break;
case'u':
case'U':
uCnt++;break;
case' ':
blank++;break;
case'\t':
t++;break;
case'\n':
n++;break;
case'f':
{
string::iterator next = iter + 1;
if(*next == 'f' ) ff++;
else if(*next == 'l') fl++;
else if(*next == 'i') fi++;
break;
}
default:break;
}
iter++;
}
cout << "aCnt: " << aCnt << endl;
cout << "eCnt: " << eCnt << endl;
cout << "iCnt: " << iCnt << endl;
cout << "oCnt: " << oCnt << endl;
cout << "uCnt: " << uCnt << endl;
cout << "blank: " << blank << endl;
cout << "t: " << t << endl;
cout << "n: " << n << endl;
cout << "ff: " << ff << endl;
cout << "fl: " << fl << endl;
cout << "fi: " << fi << endl;
}
}
(5.13)
a>
case和default后面缺少break
b>
ix需定义在switch之前
c>
case不能用逗号表示,需改为case 1 : case 3 : case 5 ...
d>
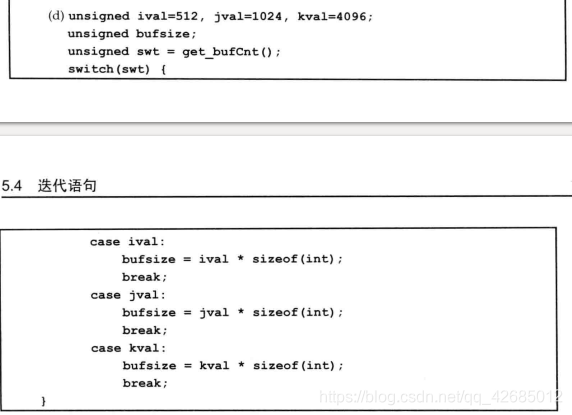
case后面需要是常量表达式,应该为const unsigned ival = 512, jval = 1024, kval = 4096;

(5.14)
void countWord() {
string line, word;
while(getline(cin, line)) {
string w;
int count = 0, n = 0;
istringstream record(line);
string before;
record >> before;
while(record >> word) {
if(word == before) {
n++;
}else {
if(n >= count) {
count = n;
w = before;
}
n = 0;
before = word;
}
}
if(n >= count) {
count = n;
w = before;
}
if(count == 0) {
cout << "没有连续单词出现过" <<endl;
}
else {
cout << w << " " << count+1 <<endl;
}
}
}

(5.15)
a>
ix作用域只在for中,需要将ix定义在for前面,if才能用
b>
for里面语句为空的时候也需要加上分号
c>
死循环
(5.16)
略
(5.17)
bool com() {
vector<int> v1 = {0, 1, 1, 2};
vector<int> v2 = {0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8};
auto max = v2.begin();
auto min = v1.begin();
while(min != v1.end()) {
if(*max != *min) return false;
max++, min++;
}
return true;
}

(5.18)
a>
do 后面的语句需要用花括号
b>
= 赋值语句,始终为真
== 才是判断语句
c>
只要ival不为0,一直循环
(5.19)
void comStr() {
cout << "请输入两个string" << endl;
string str1,str2;
cin >> str1 >> str2;
do {
if(str1.size() > str2.size()) {
cout << str2 << endl;
}
else cout << str1 <<endl;
}while(cin>>str1>>str2);
}

void printRe() {
string before, word;
bool flag = true;
cin>>before;
while(cin>>word) {
if(word == before) {
cout << "Re" << endl;
flag = false;
break;
}
if(word == "0") break;
before = word;
}
if(flag) cout << "success" << endl;
}

void printRe() {
string before, word;
bool flag = true;
cin>>before;
while(cin>>word) {
if(word == before && isupper(word[0])) {
cout << "Re" << endl;
flag = false;
break;
}
if(word == "0") break;
before = word;
}
if(flag) cout << "success" << endl;
}


while(get_size() > 0) {/*...*/}

(5.23)
void devide() {
int v1, v2;
while(cin>>v1>>v2) cout << v1/v2 <<endl;
}
(5.24)
void devide() {
int v1, v2;
while(cin>>v1>>v2) {
if(v2 == 0) throw runtime_error("除数为0");
cout << v1/v2 <<endl;
}
}
(5.25)
void devide() {
int v1, v2;
while(cin>>v1>>v2) {
try {
if(v2 == 0) {
throw runtime_error("除数为0");
}
cout << v1/v2 << endl;
}
catch(runtime_error err) {
cout << err.what() << endl;
cout << "Try again or Give up, Enter Y to continue " << endl;
char c;
cin>>c;
if(c != 'y' && c != 'Y') break;
cout << "agin:" << endl;
}
}
}





