Primer C++笔记记录(第十七章)
本书为Primer C++ 中文第五版
练习题笔记

(17.1)
(17.2)
namespace t1 {
void test1() {
tuple<int, int, int> threeInt(10, 20, 30);
cout << get<0>(threeInt) << " " << get<1>(threeInt)
<< " " << get<2>(threeInt) << endl;
}
void test2() {
tuple<string, vector<string>, pair<string, int>> Tp;
string s = "hello world";
vector<string> vs = {"HELLO", "WORLD"};
pair<string, int> psi = make_pair("ha", 1);
Tp = make_tuple(s, vs, psi);
cout << get<0>(Tp) << " " << get<1>(Tp).size() << " " << get<2>(Tp).first << endl;
}
}
(17.3)
用tuple代替QueryResult类之后,更简洁方便,但是不易扩展
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <memory>
#include <map>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
typedef vector<string>::size_type line_no;
typedef tuple<string, shared_ptr<set<line_no>>, shared_ptr<vector<string>>> result_tuple;
class TextQuery {
public:
TextQuery(ifstream&);
result_tuple query(const string &) const;
private:
shared_ptr<vector<string>> file;
map<string, shared_ptr<set<line_no>>> wm;
};
ostream &print(ostream & os, const result_tuple &qr) {
os << get<0>(qr) << " occurs " << get<1>(qr)->size() << " "
<< (((get<1>(qr)->size()) > 1)? " times " : " time ") << endl;
for(auto num : *(get<1>(qr))) {
os << "\t(line " << num + 1 << ") "
<< *(get<2>(qr)->begin() + num) << endl;
}
return os;
}
TextQuery::TextQuery(ifstream &is) : file(new vector<string>) {
string text;
while(getline(is, text)) {
file->push_back(text);
int n = file->size() - 1;
istringstream line(text);
string word;
while(line >> word) {
auto &lines = wm[word];
if(!lines)
lines.reset(new set<line_no>);
lines->insert(n);
}
}
}
result_tuple TextQuery::query(const string &sought) const {
static shared_ptr<set<line_no>> nodata(new set<line_no>);
auto loc = wm.find(sought);
if(loc == wm.end())
return result_tuple(sought, nodata, file);
else
return result_tuple(sought, loc->second, file);
}
int main() {
ifstream fin;
fin.open("test.txt");
TextQuery tq(fin);
string s;
while(cin>>s && s != "q") {
result_tuple qr = tq.query(s);
print(cout, qr);
}
}

//简洁版Sales_data
struct Sales_data {
Sales_data() = default;
Sales_data(string s): isbn(s), sales(0), all_price(0.0) { }
Sales_data(string s, unsigned sa, double p): isbn(s), sales(sa), all_price(p) { }
string isbn;
unsigned sales;
double all_price;
friend Sales_data operator+(const Sales_data &lhs, const Sales_data &rhs) {
Sales_data sum = lhs;
sum.sales += rhs.sales;
sum.all_price = sum.all_price + rhs.all_price;
return sum;
}
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Sales_data& s) {
os << s.isbn << " " << s.sales
<< " " << s.all_price << " " << s.all_price/s.sales;
}
};
bool compareIsbn(const Sales_data &lhs, const Sales_data &rhs) {
return lhs.isbn < rhs.isbn;
}
//测试函数
void test() {
Sales_data sd0("TLBB", 3, 30), sd1("TLBB", 5, 45), sd2("SJ", 8, 64);
vector<Sales_data> vsd0, vsd1, vsd2;
vsd0.push_back(sd0);
vsd0.push_back(sd2);
vsd0.push_back(sd1);
vsd1.push_back(sd1);
vsd2.push_back(sd2);
sort(vsd0.begin(), vsd0.end(), compareIsbn);
vector<vector<Sales_data>> vvsd = {vsd0, vsd1, vsd2};
reportResults6(cin, cout, vvsd);
}
(17.4)
/**** test 4 ****/
typedef tuple<vector<Sales_data>::size_type,
vector<Sales_data>::const_iterator,
vector<Sales_data>::const_iterator> matches;
vector<matches> findBook(const vector<vector<Sales_data>> &files, const string &book) {
vector<matches> res;
for(auto it = files.cbegin(); it != files.cend(); ++it) {
auto found = equal_range(it->cbegin(), it->cend(), book, compareIsbn);
if(found.first != found.second) {
res.push_back(make_tuple(it - files.cbegin(), found.first, found.second));
}
}
return res;
}
void reportResults(istream &in, ostream &os, const vector<vector<Sales_data>> &files) {
string s;
while(in >> s && s != "q") {
auto trans = findBook(files, s);
if(trans.empty()) {
cout << s << " not found in any stores\n";
}else {
for(const auto &store : trans) {
os << "store " << get<0>(store) << " sales: "
<< accumulate(get<1>(store), get<2>(store), Sales_data(s))
<< endl;
}
}
}
}
(17.5)
/**** test 5 ****/
typedef pair<vector<Sales_data>::size_type,
pair<vector<Sales_data>::const_iterator,
vector<Sales_data>::const_iterator> > matches_pair;
vector<matches_pair>
findBook5(const vector<vector<Sales_data>> &files, const string &book) {
vector<matches_pair> res;
for(auto it = files.cbegin(); it != files.cend(); ++it) {
auto found = equal_range(it->cbegin(), it->cend(), book, compareIsbn);
if(found.first != found.second) {
res.push_back(make_pair(it - files.cbegin(),
make_pair(found.first, found.second)));
}
}
return res;
}
void reportResults5(istream &in, ostream &os, const vector<vector<Sales_data>> &files) {
string s;
while(in >> s && s != "q") {
auto trans = findBook5(files, s);
if(trans.empty()) {
cout << s << " not found in any stores\n";
}else {
for(const auto &store : trans) {
os << "store " << store.first << " sales: "
<< accumulate(store.second.first, store.second.second, Sales_data(s))
<< endl;
}
}
}
}
(17.6)
/**** test 6 ****/
struct Res {
typedef vector<Sales_data>::size_type vsst;
typedef vector<Sales_data>::const_iterator vsf;
typedef vector<Sales_data>::const_iterator vss;
vsst st; vsf f; vss s;
Res(vsst a, vsf b, vss c): st(a), f(b), s(c) { }
};
vector<Res> findBook6(const vector<vector<Sales_data>> &files, const string &book) {
vector<Res> res;
for(auto it = files.cbegin(); it != files.cend(); ++it) {
auto found = equal_range(it->cbegin(), it->cend(), book, compareIsbn);
if(found.first != found.second) {
res.push_back(Res(it - files.cbegin(), found.first, found.second));
}
}
return res;
}
void reportResults6(istream &in, ostream &os, const vector<vector<Sales_data>> &files) {
string s;
while(in >> s && s != "q") {
auto trans = findBook6(files, s);
if(trans.empty()) {
cout << s << " not found in any stores\n";
}else {
for(const auto &store : trans) {
os << "store " << store.st << " sales: "
<< accumulate(store.f, store.s, Sales_data())
<< endl;
}
}
}
}
(17.7)
使用类的话显得有点复杂了,pair只允许两个参数,而tuple可以任意几个参数。
(17.8)
会在输出打印的时候,isbn为空。

(17.9)
a和b都会把十进制转成二进制
a>0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000100000
b>00000000000011110110100110110101
c>取决于输入的string

(17.10)
(17.11)
(17.12)
(17.13)
namespace t3 {
void test10() {
vector<int> vi = {1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21};
bitset<32> bt, btmp;
for(auto i : vi) {
bt.set(i);
}
btmp[1] = 1;
cout << bt << "\n" << btmp << endl;
}
template <size_t T>
struct Test {
Test(string s): bs(s) { }
void update(size_t index, int i) {
bs[index] = i;
}
bitset<T> bs;
};
void test11() {
string s = "1010111001";
Test<10> t0(s);
cout << t0.bs << endl;
Test<100> t1(s);
cout << t1.bs << endl;
}
void test12() {
string s = "1010111001";
Test<10> t0(s);
cout << t0.bs << endl;
t0.update(1, 1);
cout << t0.bs << endl;
}
template<size_t T>
double check(const Test<T>& lhs, const Test<T>& rhs) {
bitset<T> res = lhs.bs ^ rhs.bs;
res.flip();
double grade = res.count() * 100 / T;
return grade;
}
void test13() {
string z = "1110011110", a = "1110011100";
Test<10> zl(z), answer(a);
cout << check(zl, answer) << endl;
}
}
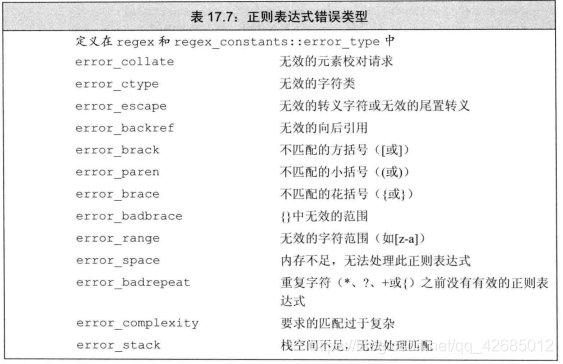

(17.14)
(17.15)
(17.16)
namespace t4 {
void test14() {
regex r("[[:alnum:]]+\\.(cpp|cxx|cc)$", regex::icase);
smatch results;
string name;
while(cin >> name && name != "q") {
if(regex_search(name, results, r))
cout << results.str() << endl;
}
}
void test15() {
regex r("[[:alpha:]]*[^c]ei[[:alpha:]]*");
smatch results;
string s;
while(cin >> s && s != "q") {
if(regex_search(s, results, r))
cout << results.str() << endl;
}
}
void test16() {
regex r("[^c]ei");
smatch results;
string s;
while(cin >> s && s != "q") {
if(regex_search(s, results, r))
cout << results.str() << endl;
}
}
}

(17.17)
(17.18)
namespace t5 {
void test17() {
string pattern("[[:alpha:]]*[^c]ei[[:alpha:]]*");
regex r(pattern, regex::icase);
string file("in at on hey read or write according to the type being handled. The input operators ignore which neighbor ha ha ha. albeit ...");
for(sregex_iterator it(file.begin(), file.end(), r), end_it; it != end_it; ++it) {
auto pos = it->prefix().length();
pos = pos > 40 ? pos - 40 : 0;
cout << it->prefix().str().substr(pos) << "\n\t\t>>> "
<< it->str() << " <<<\n" << it->suffix().str().substr(0, 40) << endl;
}
}
void test18() {
set<string> ignore = {"neighbor", "albeit"};
string pattern("[[:alpha:]]*[^c]ei[[:alpha:]]*");
regex r(pattern, regex::icase);
string file("in at on hey read or write according to the type being handled. The input operators ignore which neighbor ha ha ha. albeit ...");
for(sregex_iterator it(file.begin(), file.end(), r), end_it; it != end_it; ++it) {
if(ignore.find(it->str()) != ignore.end()) continue;
auto pos = it->prefix().length();
pos = pos > 40 ? pos - 40 : 0;
cout << it->prefix().str().substr(pos) << "\n\t\t>>> "
<< it->str() << " <<<\n" << it->suffix().str().substr(0, 40) << endl;
}
}
}

(17.19)
str(),返回一个包含输入中匹配部分的string。如果matched为false,则返回空string
(17.20)
bool valid(const smatch& m) {
if(m[1].matched)
return m[3].matched && (m[4].matched == 0 || m[4].str() == " ");
else
return !m[3].matched && m[4].str() == m[6].str();
}
void test20() {
string phone = "(\\()?(\\d{3})(\\))?([-. ])?(\\d{3})([-. ])?(\\d{4})";
regex r(phone);
string s;
while(getline(cin, s) && s != "q") {
for(sregex_iterator it(s.begin(), s.end(), r), end_it; it != end_it; ++it) {
if(valid(*it))
cout << "valid: " << it->str() << endl;
else
cout << "not valid: " << it->str() << endl;
}
}
}
(17.21)
按照21题用于判断电话号码是否合法
(17.22)
string phone = "(\\()?(\\d{3})(\\))?([-. ])?(( )*)?(\\d{3})([-. ])?(( )*)?(\\d{4})";
(17.23)
void test23() {
string mail = "(\\d{5})([-])?(\\d{4})?";
regex r(mail);
string s;
smatch results;
while(getline(cin, s) && s != "q") {
if(regex_search(s, results, r))
if((results[2].matched && !results[3].matched)) continue;
cout << results.str() << endl;
}
}

(17.24)
(17.25)
(17.26)
(17.27)
namespace t7 {
string phone = "(\\()?(\\d{3})(\\))?([-. ])?(\\d{3})([-. ])?(\\d{4})";
vector<string> vs = {"morgan (201)555-2368 862-555-0123", "drew (973)555.0130",
"lee (609)555-0132 2015550175 800.555-0000"};
regex r(phone);
void test24() {
string fmt = "$2.$5.$7";
for(auto s : vs) {
cout << regex_replace(s, r, fmt) << endl;
}
}
void test25() {
smatch results;
string fmt = "$2.$5.$7";
for(auto s : vs) {
regex_search(s, results, t7::r);
cout << results.prefix() << results.format(fmt) << endl;
}
}
void test26() {
string fmt = "$2.$5.$7";
for(auto s : vs) {
sregex_iterator it(s.begin(), s.end(), r), end_it;
sregex_iterator itmp = it;
cout << it->prefix() << " ";
++it;
if(end_it == it) {
cout << itmp->format(fmt) << endl;
}else {
for(it; it != end_it; ++it) {
cout << it->format(fmt) << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
}
void test27() {
string fmt = "$1-$3";
string mail = "(\\d{5})([-])?(\\d{4})?";
regex r(mail);
string s;
smatch results;
while(getline(cin, s) && s != "q") {
if(regex_search(s, results, r))
cout << results.format(fmt) << endl;
}
}
}

#include <random>
(17.28)
void test28() {
default_random_engine e;
for(int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
cout << e() << endl;
}
}
(17.29)
void test29(unsigned s) {
default_random_engine e;
e.seed(s);
for(int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
cout << e() << endl;
}
}
(17.30)
void test30(unsigned min, unsigned max) {
static uniform_int_distribution<unsigned> u(min, max);
static default_random_engine e;
for(int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
cout << u(e) << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test30tmp() {
for(int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
test30(0, 9);
}
}

(17.31)
//uniform_int_distribution<double> u(0, 1); 生成0-1的随机浮点数
//normal_distribution<> n(4, 1.5); 均值4,标准差1.5
//bernoulli_distribution b; 返回true的概率为0.5
void test31() {
string resp;
default_random_engine e;
bernoulli_distribution b;
do {
bool first = b(e);
cout << (first? "We go first" : "You get to go first") << endl;
} while(cin >> resp && resp != "q");
}
因为引擎返回相同的随机数序列,所以必须在循环外声明引擎对象。否则,每步循环都会创建一个新引擎,
从而每步循环都会生成相同的值。类似的,分布对象也要保持状态,所以也应该在循环外定义。
(17.32)
error: ‘resp’ was not declared in this scope
(17.33)
利用test30把转换方式的个数传进去,随机返回一个进行转换。

(17.34)
void test34() {
cout << "before boolalpha: " << true << " " << false
<< "\nafter boolalpha: "
<< boolalpha << true << " " << false << noboolalpha << endl;
cout << showbase
<< "default: " << 20 << " " << 1024
<< "\nin octal: " << oct << 20 << " " << 1024
<< "\nin hex: " << hex << 20 << " " << 1024
<< "\nin decimal: " << dec << 20 << " " << 1024
<< "\n" << noshowbase;
cout << showbase << "before uppercase: " << hex << 20
<< "\nafter uppercase: "
<< uppercase << 20 << nouppercase << noshowbase << dec << endl;
cout << "before showpoint: " << 10.0
<< "\nafter showpoint: " << showpoint << 10.0 << noshowpoint << endl;
cout << "before showpos: " << 10.0
<< "\nafter showpos: " << showpos << 10.0 << noshowpos << endl;
cout <<"default: " << cout.precision() << " " << sqrt(2.0) << endl;
cout.precision(12);
cout <<"precision: " << cout.precision() << " " << sqrt(2.0) << endl;
cout << setprecision(3);
cout <<"other precision: " << cout.precision() << " " << sqrt(2.0) << endl;
cout.precision(6);
cout << "default format: " << 100*sqrt(2.0)
<< "\nscientific: " << scientific << 100*sqrt(2.0)
<< "\nfixed decimal: " << fixed << 100*sqrt(2.0)
<< "\nhexadecimal: " << hexfloat << 100*sqrt(2.0)
<< "\nuse default: " << defaultfloat << 100*sqrt(2.0) << endl;
int i = -16;
double d = 3.14159;
cout << "i: " << setw(12) << i << "next col" << '\n'
<< "d: " << setw(12) << d << "next col" << '\n';
cout << left
<< "i: " << setw(12) << i << "next col" << '\n'
<< "d: " << setw(12) << d << "next col" << '\n'
<< right;
cout << right
<< "i: " << setw(12) << i << "next col" << '\n'
<< "d: " << setw(12) << d << "next col" << '\n';
cout << internal
<< "i: " << setw(12) << i << "next col" << '\n'
<< "d: " << setw(12) << d << "next col" << '\n';
cout << setfill('#')
<< "i: " << setw(12) << i << "next col" << '\n'
<< "d: " << setw(12) << d << "next col" << '\n'
<< setfill(' ');
cout << setbase(8);
cout << "setbase(8) 12: " << 12 << '\n';
cout << setbase(10);
cout << "please input: " << endl;
char ch;
cout << "before: \n";
while(cin >> ch && ch != 'q') cout << ch;
cout << "\nafter noskipws";
cout << "please input again: " << endl;
cin >> noskipws;
while(cin >> ch && ch != 'q') cout << ch;
cin >> skipws;
}
(17.35)
void test35() {
cout << hexfloat << uppercase << 100*sqrt(2.0) << defaultfloat << nouppercase << endl;
}
(17.36)
void test36() {
cout << setw(20) << left << "default format: "
<< setw(20) << right << 100*sqrt(2.0) << '\n'
<< setw(20) << left << "scientific: "
<< setw(20) << right<< scientific << 100*sqrt(2.0) << '\n'
<< setw(20) << left << "fixed decimal: "
<< setw(20) << right<< fixed << 100*sqrt(2.0) << '\n'
<< setw(20) << left << "hexadecimal: "
<< setw(20) << right<< hexfloat << 100*sqrt(2.0) << '\n'
<< setw(20) << left << "use default: "
<< setw(20) << right<< defaultfloat << 100*sqrt(2.0) << endl;
}

(17.37)
void test37() {
ifstream fin("test.txt");
char sink [100];
while(fin.getline(sink, 100)) {
cout << sink << endl;
}
}
(17.38)
void test38() {
ifstream fin("test.txt");
char sink [100];
while(fin.getline(sink, 100, ' ')) {
cout << sink << endl;
}
}
(17.39)
void test39() {
fstream inOut("test.txt", fstream::ate | fstream::in | fstream::out);
auto end_mark = inOut.tellg(); //记录源文件尾位置
inOut.seekg(0, fstream::beg); //重定位到文件开始
size_t cnt = 0; //字节数累加器
string line; //保存输入中的每行
//继续读取的条件:还未遇到错误且还在读取原数据
while(inOut && inOut.tellg() != end_mark && getline(inOut, line)) {
cnt += line.size() + 1; //+1表示换行符
auto mark = inOut.tellg(); //记住读取位置
inOut.seekp(0, fstream::end); //将写标记移动到文件尾
inOut << cnt; //输出累计的长度
//如果不是最后一行,打印一个分隔符
if(mark != end_mark) inOut << " ";
inOut.seekg(mark); //恢复读位置
}
inOut.seekp(0, fstream::end);//定位到文件尾
inOut << "\n";
}





